Table of Contents
AQL standards for Acceptable Quality Level, according to the standard definition of ISO 2859-1:1999: “quality level that is the worst tolerable process average when a continuing series of lots is submitted for acceptance sampling”.
For example, AQL 2.5% means that I hope the defective products of the whole order will not exceed 2.5%.
It mainly solves two questions:
- How many samples should be taken for inspection?
- In case of defective products, what quantity is acceptable?
In short, it is not only a statistical method, but also a standard. It is widely used in all walks of life.
Key concepts
Before understanding the AQL table, we must first understand 3 concepts:
- Lot: refers to the total quantity of orders.
- Inspection level: There are different inspection levels, and they require different sampling quantities. What inspection level needs to be selected depends on the specific industry and product application. Normally the default is level II.
- AQL Limit: this parameter determines whether the whole lot of products can be qualified.
AQL Defects
Meanwhile, it is necessary to understand the definition of AQL defects.
Defect means failure to meet customer quality requirements, in practice, there are three types of defects.
- 0% for Critical defects: completely unacceptable, the user may be harmed, or the product does not comply with relevant laws and regulations.
- 2.5% for Major defects: This type of defect is usually not accepted by end-users because it may cause failure.
- 4% for Minor defects: This kind of defect does not reduce the usability of the product, but it does not meet the specifications, but most customers may not mind.
How to determine the above defects depends on the specific industry and product use. For example, the medical and aircraft industries are very demanding, because defective products may cause health or life risks.
How to read
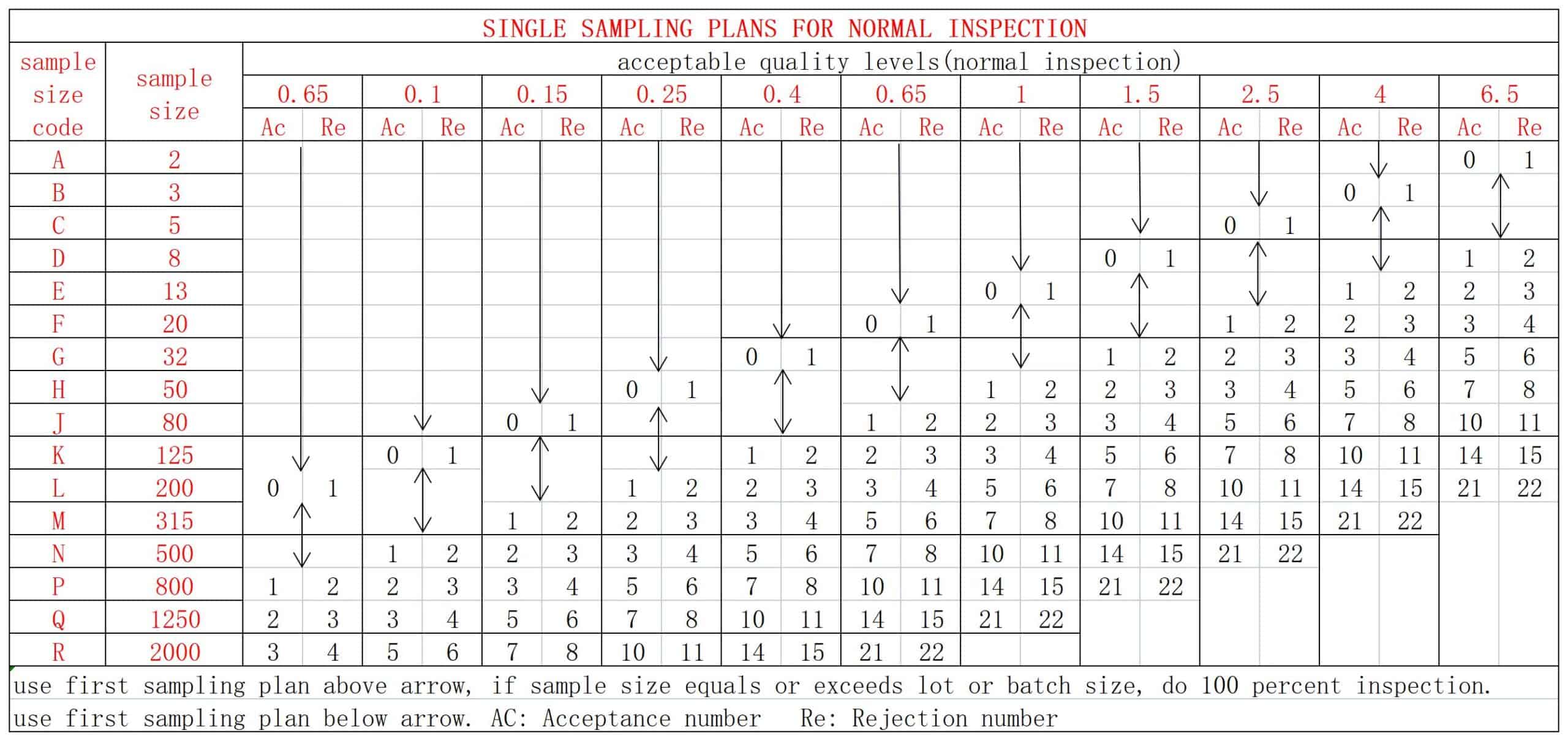
AQL has two tables, one(table A) is to find code according to the lot size, the other(table B) indicates the sample size and the maximum acceptable number of defects.
For example, if the order quantity is 20,000, we choose general inspection level II as the sampling method, so that we can get the code is “K” from table A.
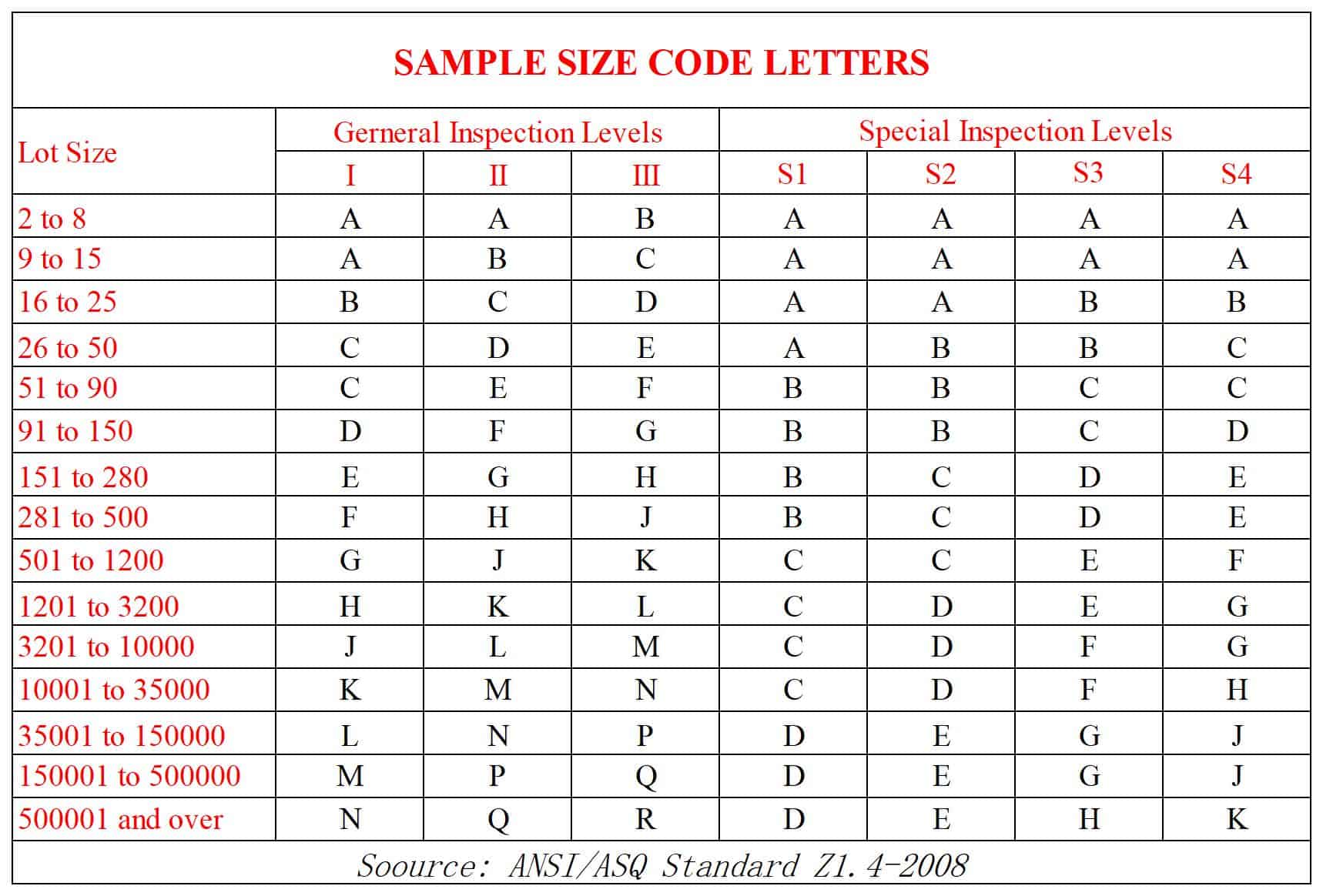
Corresponding to Form B, the sample number obtained is 125. Generally, we choose the AQL 2.5, then we can know that the acceptable number of major defects is 7, the rejected number is 8, and the acceptable number of minor defects is 10, the rejected number is 11.
Can AQL guarantee zero defects of goods
Obviously, the answer is not. You can’t ensure zero defects for the entire batch through AQL. AQL stands for “acceptable quality limit” and it is not designed to ensure zero defects.
If you want to ensure zero defects, you can only check 100%, but this is expensive and impractical. This is also the reason why AQL is popular.



