Surfactants are substances that cause a significant reduction in the surface tension of the target solution and are an essential component of detergents, which are added to remove dirt from the skin, clothing, and household products.
Surfactants have been called “industrial MSG” and without them, the cosmetics industry would probably not exist.
How surfactants work
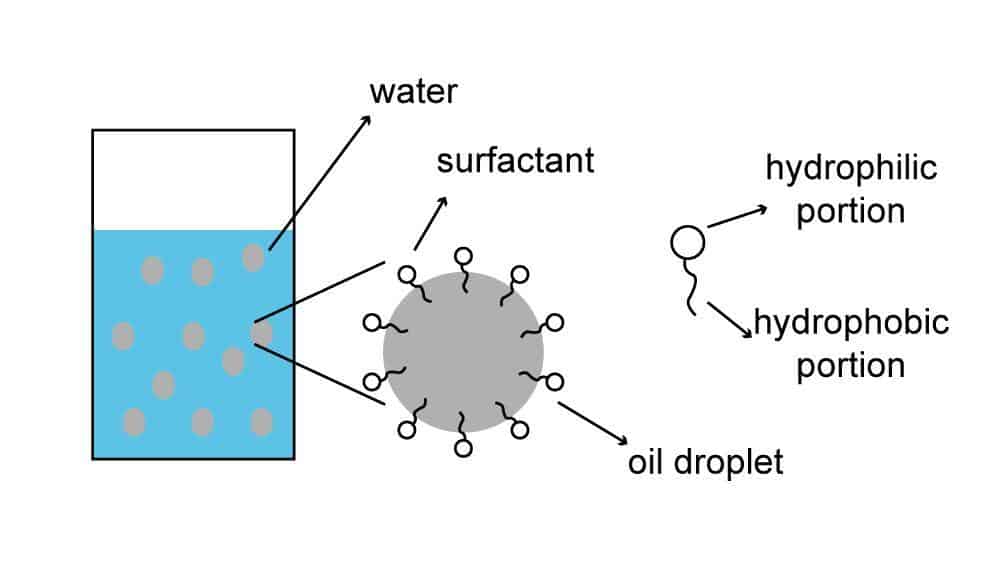
Surfactants have both hydrophilic and lipophilic groups in their molecules, a property also known as amphiphilic.
Due to this amphiphilic property, they can form micelles in water at appropriate concentrations – the hydrophilic head is attracted outward by water, and the lipophilic tail is repelled by water and thus faces inward.
These micelles have an important role in skin care products.
During cleansing, oil stains are pulled by the lipophilic groups to the inside of the micelle, and the whole micelle is carried away by water. In an oily environment, they can form an inverse micelle, where the head is inside and the tail is outside.
The strength of surfactant and the size of critical micelle concentration are closely related to its hydrophilicity, and the hydrophilicity is determined by the interaction and joint determination of hydrophilic and lipophilic groups, for this reason, Griffin proposed to express the hydrophilicity of surfactants by the hydrophilic-lipophilic balance (HLB), which is a measure of the degree of balance between hydrophilic and hydrophobic groups in terms of size and strength.
Application of surfactants in cosmetics
Most people may think of surfactants primarily as a cleaning agents, but their applications may go beyond our imagination.
Cleaning
The most widespread and useful basic characteristic of surfactants is their detergent and decontamination action, which can “wrap” various kinds of dirt and wash it off through adsorption, wetting, penetration, emulsification and dispersion. The ability to remove dirt lies in its ability to wet the surface of the stain and emulsify it, that is, to “wrap” the oil and let it emulsify in the water and be washed off.
Foaming
Foaming is a directional arrangement of surfactants in the interfacial layer or surface through the insertion of hydrophilic groups into the aqueous phase while the lipophilic groups are inserted into the oil phase or erected in the air, which reduces the interfacial tension, thus prompting the formation of small bubbles of air in the liquid and ensuring that the bubbles rise to form a foam layer. A large amount of foam can help the dirt out of the cleaning target to rise to the liquid surface. However, a lot of foam may only be due to the auxiliary role of the foaming agent and is not directly related to the cleaning ability.
Emulsifying
Yes, the emulsifier as we know it broadly belongs to the surfactant, which enables the immiscible oil and water phases to mix to form a homogeneous mixture. In the emulsification process, the lipophilic end of the surfactant molecule dissolves into the oil phase, the hydrophilic end dissolves into the water phase, and other molecules are adsorbed at the interface between oil and water, thus reducing the interfacial tension between oil and water and enabling it to be fully emulsified.
Solubilization
Surfactants can increase the solubility of some insoluble substances in water so that they are completely dissolved in water and eventually form a transparent state, and this effect is called solubilization. When surfactants are added to water, the surface tension of water drops sharply at first, and then micelles of active agent molecules are formed. When the concentration of surfactant reaches the critical micelle concentration, the micelle can absorb the oil or solid particles at the end of the lipophilic group. Therefore, the solubility of slightly soluble or insoluble substances is increased.
Dispersion
Surfactants are able to disperse solid particles evenly and stably in cosmetics to maximize the whitening, concealing, and sunscreen effects of powders. During the dispersion process, the hydrophilic end of the surfactant molecule extends in water and the lipophilic end adsorbs on the surface of the solid particles. A hydrophilic adsorption layer is formed on the surface of the solid. The wetting effect of the active agent destroys the cohesion between the solid particles so that the active agent molecules enter the solid particles and become small masses dispersed in the water.
Types of surfactants in cosmetics
There are many ways to classify surfactants, according to their hydrophilic groups, water-solubility, raw material sources, etc. It is generally agreed that it is more appropriate to classify surfactants according to their chemical structure.
Anionic surfactants
The hydrophilic group is anionic, i.e. it is the negatively charged ions that act after ionization in water. Anionic surfactants have the longest history of development, the largest production volume, and the most varieties, with better washing and foaming effects, mostly used in products for cleaning, but are generally more irritating. They cannot be mixed with cationic surfactants, but ok to combine with amphoteric and nonionic surfactants.
Cationic surfactants
In water, they can generate water-repellent cations. They have good surface activity only in acidic media, while they tend to precipitate and lose effect in alkaline media. They are not suitable for cleaning formulations because they do not clean, rinse, or foam, but they have a significant bactericidal effect, such as the big-name quaternary ammonium salts. because of their good soft and smooth properties, they are widely used in hair conditioners, or as soft finishing agents for fibers.
Amphoteric surfactants
These surfactants have positive and negative ionic groups in their molecular structure and can exhibit the properties of cationic or anionic surfactants in different pH media. they are weak in washing, but the effect of increasing foam, stabilizing foam, and thickening is good, mostly used as auxiliary anionic surfactants in cleaning products to enhance the cleaning effect and reduce irritation.
Non-ionic surfactants
It does not dissociate in water, the hydrophilic groups are polyols such as glycerol, polyethylene glycol and sorbitol, while the lipophilic groups are long-chain fatty acids or long-chain fatty alcohols as well as alkyl or aryl groups. It excels in emulsification and solubilization, is mostly considered an emulsifier, with low irritation, and is mostly used in creams and lotion products as well as water-based products that require solubilization. It can be applied to a wider pH range than general ionic surfactants and can be used together with other ionic surfactants.
The comment surfactants in cosmetics
Soap-based
Soap-based surfactants, which are strongly alkaline cleaning products with a pH value of 9-10, typically such as sodium laurate, sodium myristate, sodium palmitate, sodium stearate, etc., are commonly used as raw materials for soaps. The soap base has excellent lathering ability and is suitable for people with oily skin.
Because the skin of the human face in its normal state is weakly acidic (PH4.5-6.5), if you use a strong alkaline soap for a long time, it will take away too much oil from the face and lead to dehydration, and the texture of the weak alkaline has a certain destructive power on the external environment of the skin. In addition, the strong alkaline soap has too strong cleaning ability, easy to make the skin cells and cells to wash away the oil, resulting in dry or inflamed skin.
Sulfate salts
With a better cleaning ability and weak alkalinity, more effective than soap-based surfactants, the famous Sodium lauryl sulfate (SLS) belongs to these products. Mainly extracted from petroleum, so they have a very unpleasant odor, dark color, and fast bacterial growth, short shelf life.
In addition, most of them contain fatty acid sulfate salts, which are insoluble in water and difficult to rinse off, are easily left on the surface of human skin, causing many skin problems.
Moreover, the wastewater from the use of petroleum-based products is difficult to be degraded when it enters the water, which can cause environmental pollution.
Alkyl polyglucoside(APG)
It is a new type of nonionic surfactant with comprehensive performance, which is synthesized from renewable resources of natural fatty alcohols and glucose and has the advantages of common nonionic and anionic surfactants: high surface activity, good ecological safety, and compatibility. Typically such as Dodecyl Glucoside.
It’s the preferred “green” surfactant, has the tendency to replace the existing petroleum-based as the mainstream surfactants. But the price is higher than traditional surfactants and the detergency is slightly inferior, mostly used in combination with AES and CAB.
Betaines(CAB)
It is a class of amphoteric surfactants with good application performance. Water hardness does not affect betaine surfactant, it produces good foam and good stability in both soft and hard water. Typically such as Cocoamidopropyl Betaine.
In practical application, its performance in washing, emulsification, and wetting is good, but the irritation is slightly high, thus, to a certain extent, limiting its application in personal care products.
Amino acid-based
Amino acid-based surfactants are amphoteric and have better “conditions” in all aspects. Typically such as Sodium Lauroyl Glutamate.
From the safety point of view, it is a safe raw material with a PH value between 5.5 and 6.5, which is weakly acidic and close to the PH value of human skin, so it is mild and skin-friendly and does not irritate the eyes; easily soluble in water and rinsed off, will not remain on the surface of the skin and cause harm to human skin.
From the aspect of environmental protection, amino acid-based is non-toxic and non-hazardous, with good biodegradability. After a period of time, the sewage after use can be completely degraded by water microorganisms into carbon dioxide, water, and other components, which will not cause pollution to water and the natural environment.
Alkylammonium salts
This type of surfactant is highly alkaline, does not produce free amines in alkaline solutions, very stable. Easily soluble in water, transparent, just a few parts per million has sterilization and disinfection ability. Typically such as Polyquaternium.
It is non-toxic, non-corrosive to metal, and stable even in boiling water. Mainly used as a disinfectant and hair conditioner. At the same time, it can be used as an antistatic agent, softener, retarding agent, and color fixing agent of fiber.
| Types | Kinds | Product | Application | Foaminess | Texture | Viscosity | Gentle |
| Anionic | Soap-based | Sodium Stearate | cleaning | ★★★ | ★★★★ | ★★★ | ★★★ |
| Sulfate Salts | Sodium lauryl sulfate | cleaning | ★★★ | ★★★★ | ★★★ | ★★★ | |
| Cationic | Alkylammonium Salts | Polyquaternium | Hair Condition | ★★★★ | ★★★★★ | ★★★★★ | ★ |
| Non-ionic | Alkyl Polyglucoside | Dodecyl Glucoside | Mild cleaning | ★★ | ★★ | ★ | ★★★★★ |
| Amphoteric | Betaines | Cocoamidopropyl Betaine | Mild cleaning | ★★★★★ | ★★★★★ | ★★★★★ | ★★★★ |
| Amino acid-based | Sodium Lauroyl Glutamate | Mild cleaning | ★★★★★ | ★★★★★ | ★★★★★ | ★★★★ |
Which surfactants are better
You can evaluate a surfactant in the following three ways:
- Natural: That is, the origin of the substance, which comes from natural substances or their derivatives, it is a sustainable source, but not industrially extracted or synthesized, with no damage to the environment.
- Low irritation: This refers to the hazards to the human body during use, including allergies, toxicity, skin residues, etc. Scientists have spent a lot of time and effort studying this, you can visit CIR for specific information.
- Environmentally friendly: This refers to the biodegradability of the substance, whether it will break down into harmful substances after use, or whether it will not degrade and thus pollute the environment. In Western Europe, the surfactant component of all household detergents must be biodegradable, people are concerned that surfactants can be “recycled” into drinking water.
In summary, amino acid surfactants are the best but are not widely used due to their high price and poor cleaning performance (often requiring compounding with others). In real-world applications, Alkyl polyglucoside is more popular and has better overall performance.
How to choose a surfactant
There is no doubt that natural is the best, but there is no way for a final product to be considered only natural. It needs to be considered from multiple perspectives such as raw materials, formulation, process, packaging, performance, and even price.
First is the interaction between the ingredients. Surfactants are critical to ensure viscosity control, color, odor, pH, salt content, and foaming/cleaning properties. For example, some very good surfactants are not suitable in acidic systems, or the product is not viscous enough, or the cleaning effect is not as expected.
In addition is the positioning of the product, or selling point. If your main focus is natural, then it is best to choose natural ingredients, which are the current mainstream of the market. If you go for the general sales, then of course the cheaper the ingredients the better, as far as regulations allow, so that your prices are competitive.
Finally, regulation, which is crucial, different country are inconsistent, the restrictions/limits are also inconsistent, the most stringent restrictions on cosmetic surfactants is currently Prop 65, in which EDA, MEA, TEOA are prohibited from being added.



